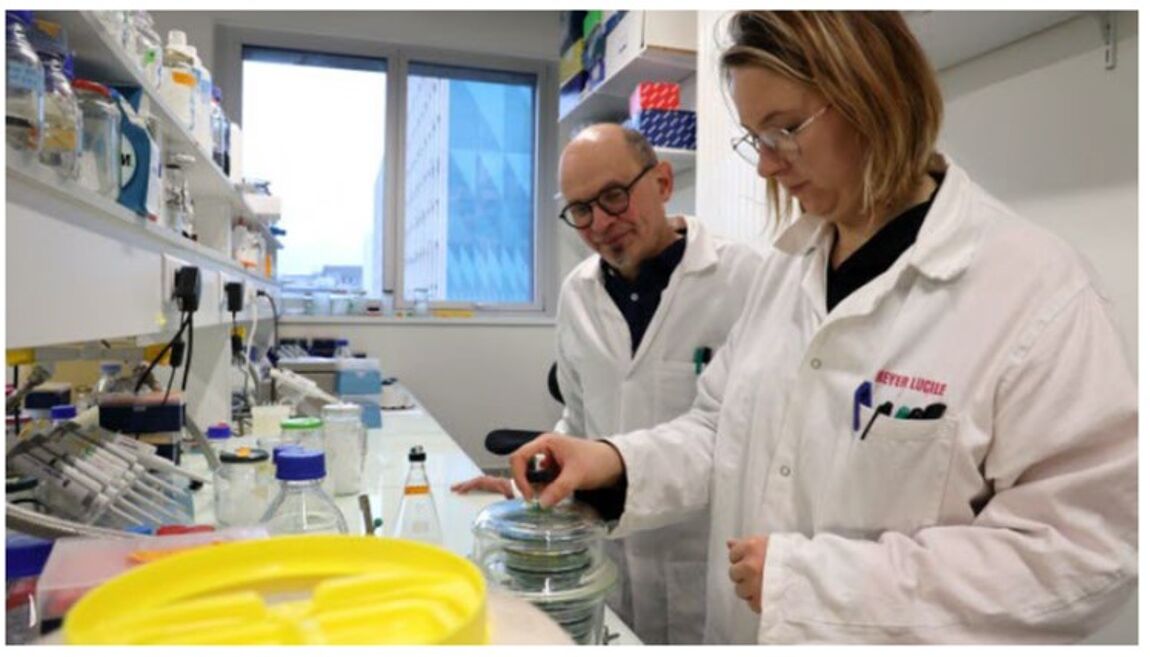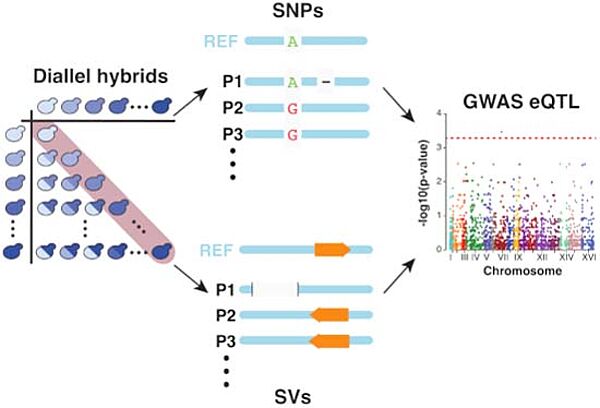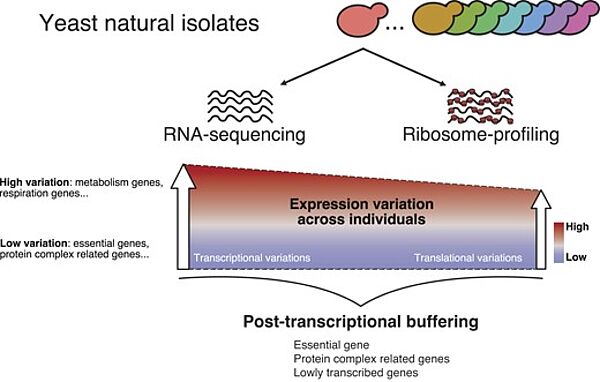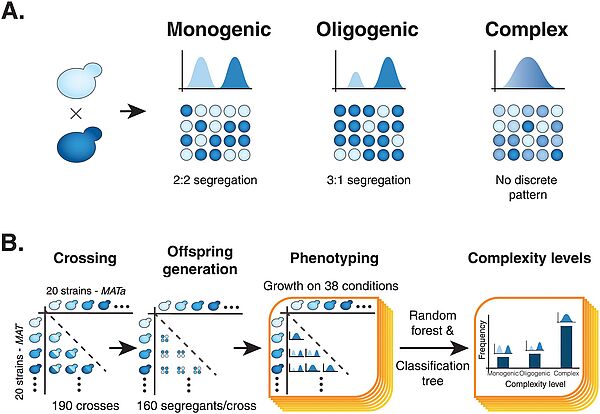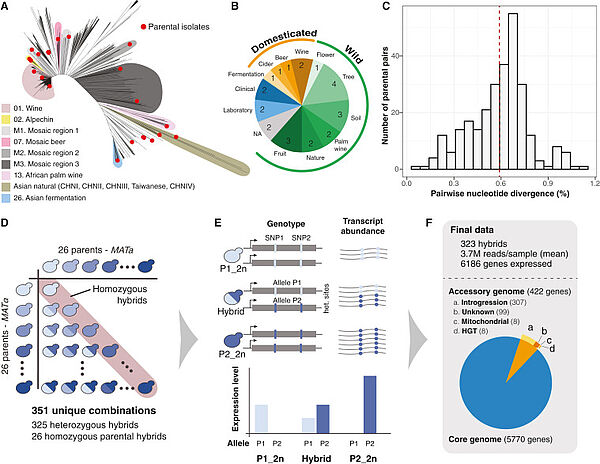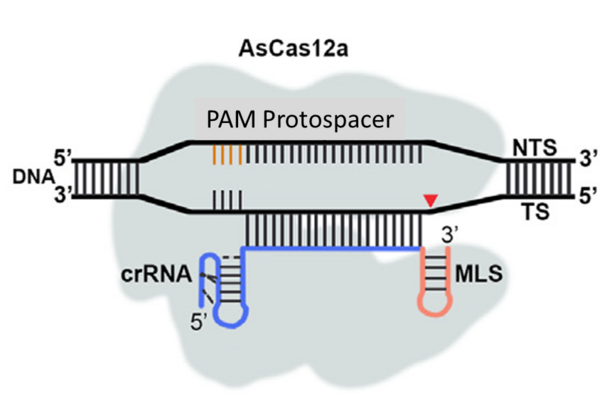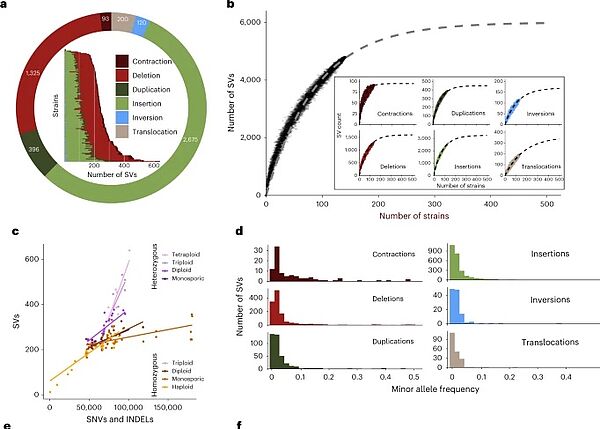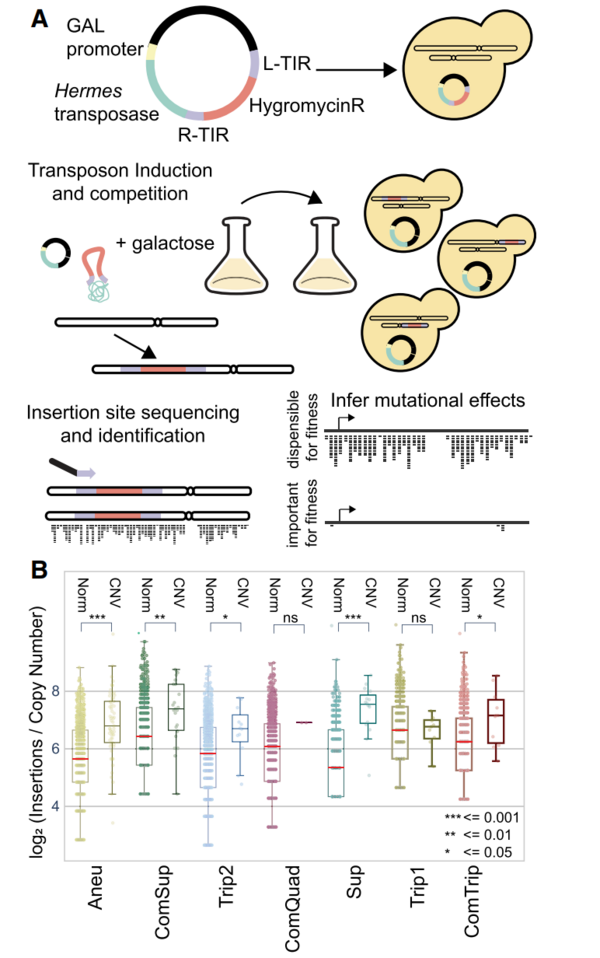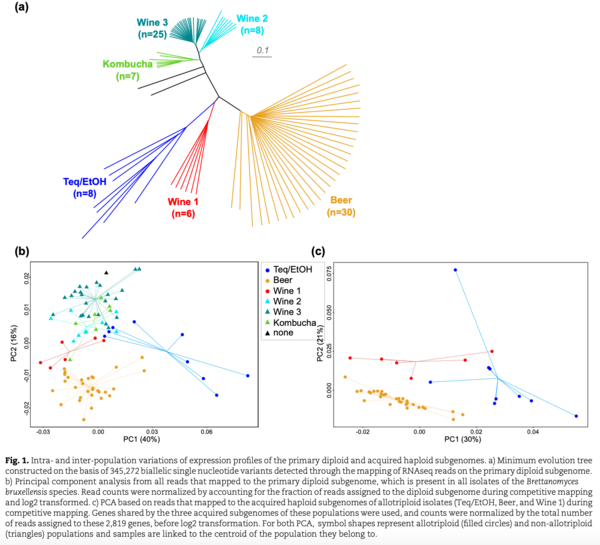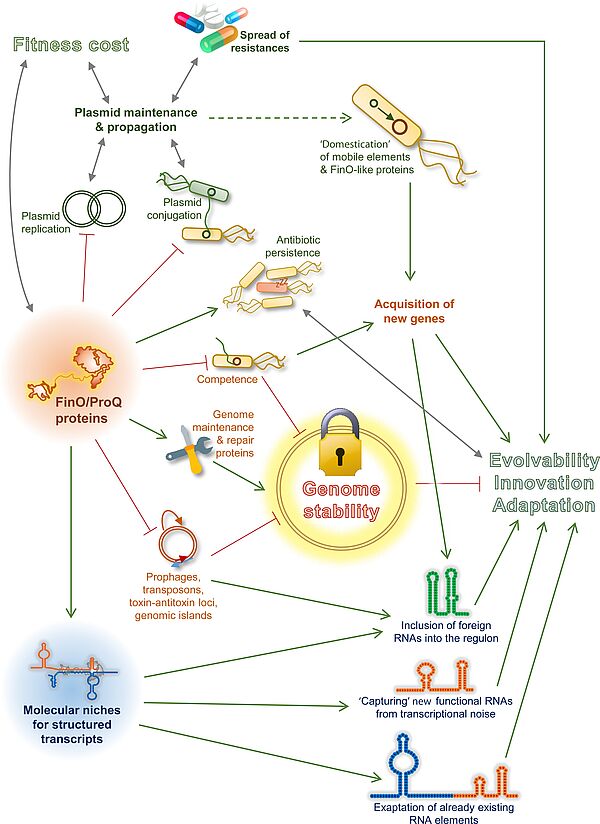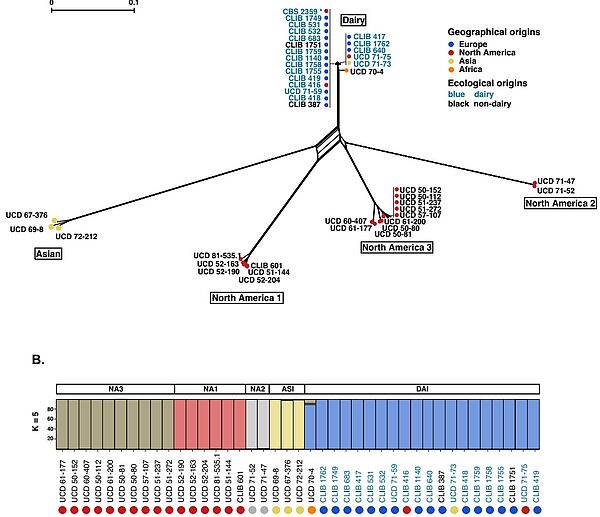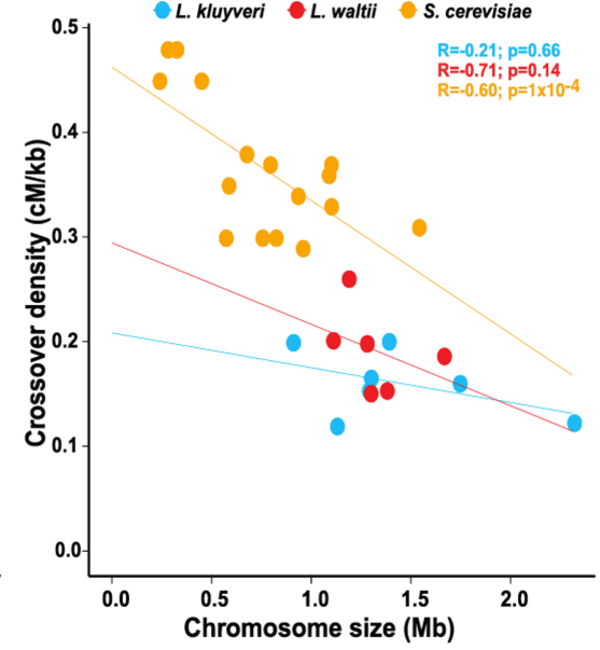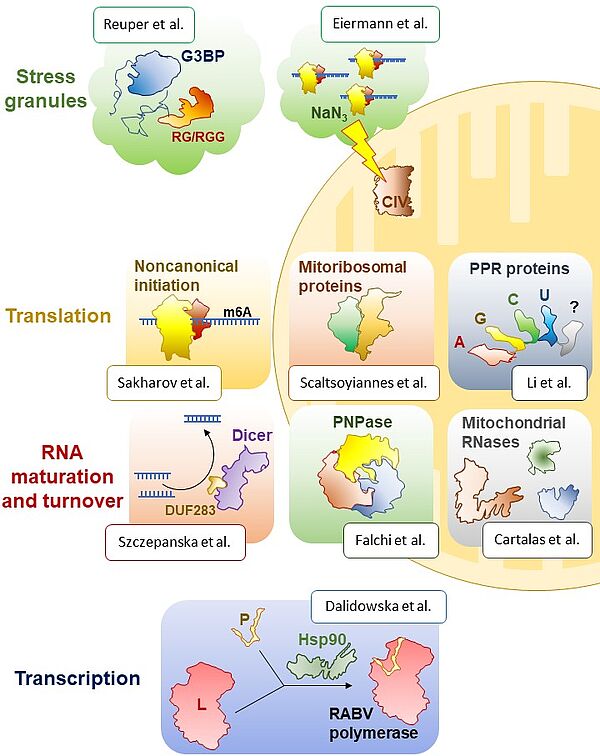
Nouvelle publication en collaboration
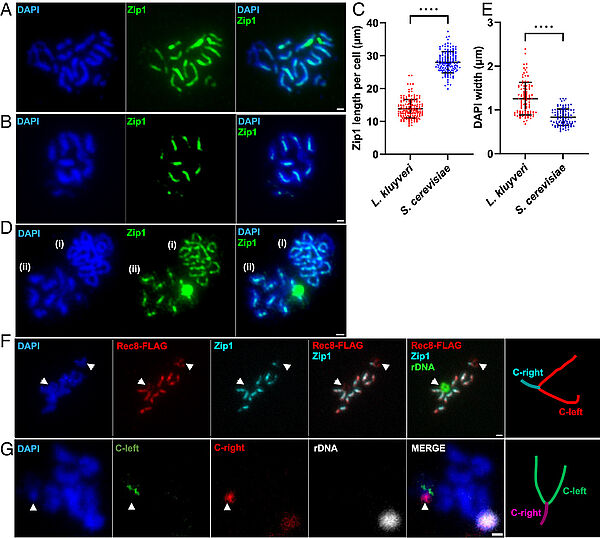
Absence of chromosome axis protein recruitment prevents meiotic recombination chromosome-wide in the budding yeast Lachancea kluyveri. Sylvain Legrand, Asma Saifudeen, Hélène Bordelet, Julien Vernerey, Arnaud Guille, Amaury Bignaud, Agnès Thierry, Laurent Acquaviva, Maxime Gaudin, Aurore Sanchez,…